Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) and Customer Relationship Management (CRM) are vital business tools with distinct roles: ERP integrates and streamlines internal processes like finance, HR, and supply chain management to boost operational efficiency, serving as a company’s backbone, while CRM focuses on customer interactions, enhancing sales, marketing, and support to drive revenue and loyalty, acting as the business’s face.
ERP suits complex organizations needing process synchronization (e.g., manufacturers), whereas CRM fits sales- and customer-driven firms (e.g., e-commerce); however, integrating both—such as Salesforce with SAP—offers a seamless flow between customer insights and operational execution, maximizing efficiency and growth.
This blog dives deep into ERP and CRM, exploring their definitions, functionalities, benefits, and how businesses can decide which one—or both—fits their needs.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat is ERP?
ERP means Enterprise Resource Planning to keep businesses running smoothly. These “all-in-one” platforms eliminate the need for different components of a business to live in their own digital environments. An ERP system takes care of:
- Operations and finance, and accounting
- Management of inventory and supply chain
- Human resources tasks
- Manufacturing processes
- Purchasing and vendor relationships
- Asset management
- Business intelligence report
You can consider ERP the central nervous system of your business – it ensures that all internal functions align smoothly.
What is CRM
Customer Relationship Management (CRM) is a software solution focused on managing customer interactions, improving relationships, and boosting sales and marketing efforts. It helps businesses enhance customer satisfaction and drive revenue growth.
- Managing customer data
- Tracking sales pipelines
- Automation of marketing campaigns
- Coordinate customer service efforts
- Managing leads
- Maintaining a history of contact
- Examining KPIs
CRM system — your new and improved digital Rolodex — that remembers everything about your interaction with every customer, what they love, and when they bought it, and automates follow-ups and engagement.
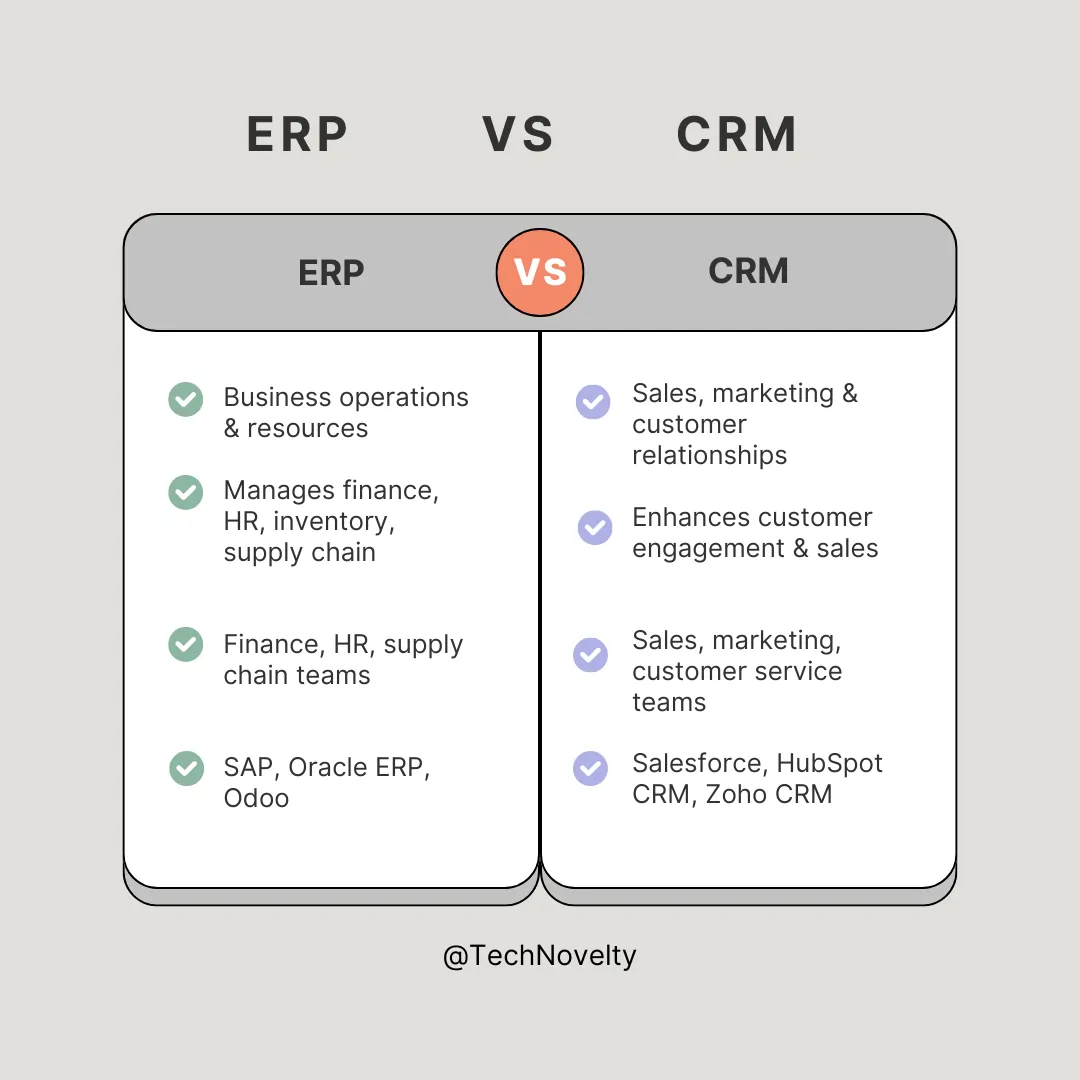
The key difference between ERP and CRM is what they primarily focus on:
ERP systems improve internal operations and resource management, whereas CRM systems enhance external relationships and revenue opportunities.
To get a complete view, many businesses use both together. There is no doubt that ERP does the behind-the-scenes activities to keep our businesses running, while CRM focuses on the front-facing activities that drive growth and keep customers happy.
Key Differences Between ERP and CRM Systems
ERP and CRM systems serve distinct purposes within a business ecosystem, each focusing on specific operational areas:
1. Internal vs External Focus
- ERP systems manage internal business processes:
- Financial accounting and reporting
- Supply chain operations
- Manufacturing workflows
- Human resources management
- Inventory control
- CRM systems handle external relationships:
- Customer interaction tracking
- Sales pipeline management
- Marketing campaign execution
- Service delivery monitoring
- Lead nurturing
2. Data Management Approach
ERP centralizes operational data:
- Resource allocation metrics
- Production schedules
- Financial transactions
- Inventory levels
CRM organizes customer-centric information:
- Purchase history
- Communication records
- Service requests
- Sales opportunities
3. User Base Differences
ERP users typically include:
- Finance teams
- Operations managers
- Supply chain personnel
- HR departments
CRM users primarily consist of:
- Sales representatives
- Marketing teams
- Customer service staff
- Account managers
Both internal efficiency and customer-facing operations are critical for firms; this is where the relationship between CRM and ERP holds a lot of value. Similar to ERP systems optimising business processes, CRM systems improve customer engagement and help increase sales through better relationship management.
Market Trends: ERP and CRM Software Solutions
The software solutions market is experiencing significant growth for both ERP and CRM systems. Both ERP and CRM systems have seen significant growth in the software solution market.
ERP Market Trends
The global ERP market was valued at $42.4 billion in 2019 and is projected to reach $78.41 billion by 2026. This growth is driven by:
- Transformation of industries through digital initiatives
- Growth in the demand for cloud-based ERP solutions
This can take the form of
- AI & machine learning capabilities
- Creating mobile ERP apps for remote work workforce management
CRM Market Trends
Meanwhile, the CRM market has even more growth potential, with estimates of $96.5 billion in value by 2028. The following elements are driving this growth:
- More focus on creating unique consumer experiences
- Use of tools for AI-powered customer analytics
- Social CRM platforms are on the rise
- Integration of advanced automation tools in CRM systems
Recent Market Research Findings
Studies conducted over the last year show areas of preference shifting in both the ERP and CRM areas:
ERP Market Trends
- Migration from legacy systems to cloud-based solutions
- Customizations of ERP systems to cater to specific industries
- Implementation of enhanced security features in ERP software
- Availability of real-time analytics capabilities in ERP systems
CRM Market Trends
- Emergence of mobile-first CRM platforms
- Use of predictive analytics to understand customer behavior
- Integration of social media platforms with CRM systems
- Compliance with data privacy regulations through enhanced features
The growth exhibited by both the ERP and CRM markets is a testament to the awareness that organisations are developing regarding the necessity of using specialised software tools to handle their internal processes and customer interactions.
Key ERP system Features for Operational Efficiency
ERP systems come loaded with powerful functionalities that are designed to optimize business processes and improve productivity across departments. Here is a deep dive into the key ERP system features that make this system an indispensable tool:
1. Financial Management
- Real-time accounting and bookkeeping
- Automated billing and invoicing
- Budget tracking and forecasting
- Tax management and compliance tools
- Multi-currency support
2. Order Processing
- Purchase order automation
- Order status tracking
- Supplier management
- Contract management
- Payment processing integration
3. Inventory Management
- Real-time stock level monitoring
- Automated reordering systems
- Warehouse management
- Batch tracking
- Supply chain visibility
4. Production Planning
- MRP (material requirements planning)
- Production scheduling
- Quality control monitoring
- Resource allocation
- Capacity planning
This can be accomplished through integration to eliminate data silos and reduce manual intervention: The automation capabilities reduce human error while accelerating development and processes across departments. Accessing real-time data allows for quicker decision-making and helps recognize bottlenecks before they affect operations.
Modern ERP systems also encompass customizable dashboards and reporting tools that provide actionable insights into business performance. This visibility allows organizations to optimise their processes and stay competitive in their markets.
Key CRM Features for Customer Engagement
Modern CRM capabilities reshape the ways companies interact with customers through tools engineered for meaningful connections:
1. Contact Management and Customer Profiles
- Central storage for the customer data
- Detailed tracking of interaction history
- Industry-specific data with custom fields.
- Social media integration to understand customers better
2. Sales Pipeline Management
- Deals are tracked visually through stages
- Prioritize leads with scoring.
- Ability to forecast revenue
- Real-time sales analytics
3. Marketing Automation Tools
- Creating email campaigns and scheduling
- Qualification and lead scoring
- Marketing content A/B testing
- Automated workflow triggers
- Content delivery is personalized
4. Communication Features
- Integration at a Unified Multi-channel Conversational Messaging
- Automated response systems
- Meeting scheduling tools
- Call centre integration capabilities
5. Analytics and Reporting
- Customer behavior analysis
- Campaign performance metrics
- Custom report generation
- Building dashboards for real-time
- [ROI tracking for marketing initiatives]
Together, these CRM features form a powerful system that adjusts to new customer demands and offers insights for company development. Automation features minimize manual efforts, enabling teams to devote more time to establishing stronger customer relationships through tailored engagement.
Benefits of Implementing ERP Systems in Businesses
To understand why ERP systems are a game-changer for businesses. They provide tremendous productivity gains and strategic advantages, revolutionizing how organizations deploy their assets and make decisions.
1. Streamlined Back-End Operations
With ERP systems in place, businesses can expect:
- Automated data entry reduces manual workload by up to 80%
- Real-time inventory updates prevent stockouts and overstock situations
- Standardized processes across departments eliminate redundant tasks
- Integrated financial management accelerates month-end closing cycles
2. Enhanced Decision-Making Capabilities
The ability to analyze large amounts of data to help make better decisions.
- Real-time analytics provide instant insights into business performance
- Unified data sources ensure accurate reporting across departments
- Predictive analytics help forecast market trends and demand patterns
- Custom dashboards deliver personalized views of critical metrics
3. Cost Reduction and Resource Optimization
- Cost savings achieved by automating processes
- More efficient inventory management reduces carrying costs
- More accurate resource allocation based on actual usage data
- Reduced IT maintenance costs through a unified integrated solution
4. Compliance and Risk Management
The importance of ERP systems is highlighted when they ensure:
- Built-in audit trails provide regulatory compliance
- Standardized processes minimize human error
- Automatic updates ensure systems stay up to date with regulations
- Leverage centralized control for increased data security
These benefits contribute to a more effective organization, empowering it to work more efficiently and stand out against competitors in the market. As a result, organizations implementing ERP systems can make significant strides in operational execution and decision making.
Benefits of CRM system for Business Growth
CRM systems have transformed how businesses interact with their customers by providing powerful tools for engagement and data-based insights. These systems offer unique advantages for companies seeking to improve customer relationships and increase sales efficiency.
1. Advanced Customer Engagement Tools
CRM systems are well-equipped with efficient tools designed to help businesses interact with their customers. Some key features include:
- Automated Communication Sequences – Pre-scheduled personalized email campaigns, follow-up messages, and targeted promotions
- Unified Multi-channel Communication – Engage with customers via emails, social media, phones, and chat platforms from one single interface
- Instant Analytics — Observe customer behavior trends and participation statistics to enhance communication approaches
2. Enhanced Service Quality Through Interaction Tracking
CRM systems allow companies to tailor their offer because they use them to track customer interaction. This allows companies to:
- 360-Degree Customer Views — Up-to-date customer histories, preferences , and past interactions
- Response Time Optimization: Monitor and improve team performance in addressing customer inquiries.
- Predictive Analytics – Anticipate customer needs based on historical data and behavior patterns
3. Empowering Sales Teams with Intelligent Lead Scoring
With intelligent lead scoring features, CRM platforms enable sales teams to focus on leads that are most likely to convert. The built-in reporting features available in these systems help businesses gauge customer satisfaction levels and target areas for service improvement.
These tools create a data-driven approach to relationship building, resulting in:
- 25-30% in sales productivity increase
- Increased customer satisfaction rates by 20-30%
- 15–25% lower customer service cost
Using artificial intelligence and machine learning capabilities, organisations can automate routine tasks, such as gathering customer information or frequently asked questions, freeing customer service representatives to focus on complex issues that require human intervention.
|
ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) | CRM (Customer Relationship Management) | |
| Definition | A system that integrates and manages core business processes. | A system that focuses on managing customer interactions and sales. | |
| Primary Focus | Internal business operations, resource planning, and efficiency. | Customer acquisition, retention, and relationship management. | |
| Key Functions | Finance, supply chain, inventory, HR, procurement, manufacturing. | Sales automation, marketing, customer service, support, lead tracking. | |
| Users | Used by finance, HR, operations, and supply chain teams. | Used by sales, marketing, and customer service teams. | |
| Data Handling | Manages internal business processes and operational data. | Manages customer interactions, preferences, and sales data. | |
| Benefits | Streamlines business processes, reduces costs, improves efficiency. | Enhances customer relationships, boosts sales, and improves retention. | |
| Examples | SAP ERP, Oracle ERP, Microsoft Dynamics 365 ERP, Odoo ERP. | Salesforce, HubSpot, Zoho CRM, Microsoft Dynamics 365 CRM. | |
| Integration | Often includes CRM as a module but focuses on business-wide processes. | Can be integrated with ERP for better customer and operational synergy. | |
| Who Needs It? | Businesses needing full operational control and resource optimization. | Businesses focusing on customer engagement, sales, and marketing. |
Best ERP Use Cases for Various Industries

systems provide unparalleled value in specific industries where intricate operations require smooth integrations. Here are the sectors that gain the most from ERP implementation:
1. Manufacturing
- Production planning and scheduling
- Quality control management
- Raw material tracking
- Equipment maintenance scheduling
- Supply chain optimization
2. Healthcare
- Patient record management
- Medical inventory control
- Regulatory compliance tracking
- Staff scheduling
- Insurance claim processing
3. Retail and Distribution
- Multi-location inventory management
- Order fulfillment automation
- Warehouse operations
- Purchase order tracking
- Demand forecasting
4. Professional Services
- Project management
- Resource allocation
- Time tracking
- Billing automation
- Contract management
Businesses should consider implementing an ERP system when they experience:
- Manual data entry across multiple systems
- Lack of real-time visibility into operations
- Difficulty in scaling operations
- Increasing compliance requirements
- Need for standardized processes across departments
Best CRM Use Cases for Complex Relationships & Industries
CRM systems provide specific features that are especially useful in industries where customer interaction is key to doing business. Here are some sectors that can greatly benefit from using CRM systems:
1. Retail and E-commerce
CRM systems can help retailers and e-commerce businesses in the following ways:
- Managing customer experiences across multiple channels (online, offline, mobile)
- Keeping track of purchase histories and individual preferences
- Tailoring marketing campaigns based on customer behavior
- Implementing loyalty programs to retain customers
2. Financial Services
In the financial services industry, CRM systems can assist in:
- Maintaining comprehensive portfolios for each client
- Monitoring investment preferences and trends
- Ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements
- Recording all communications with clients for reference
3. Real Estate
Real estate professionals can use CRM systems to:
- Track property listings and client preferences
- Manage leads and potential buyers/sellers
- Schedule property viewings efficiently
- Document interactions with clients for future reference
4. Professional Services
For businesses offering professional services, CRM systems can be valuable in:
- Documenting specific project requirements from clients
- Managing timelines for service delivery
- Tracking hours spent on billable tasks
- Maintaining a history of communication with clients
A cultivated CRM system becomes essential when businesses face:
- High volume of customer interactions
- Complex sales processes or cycles
- Need for personalized service delivery
- Multiple points of contact across various channels (phone, email, social media)
- Regulatory compliance requirements specific to the industry
- Collaboration among different teams or departments within the organization
These situations require advanced customer data management that only dedicated CRM solutions can offer.
Integrating ERP and CRM for Business Efficiency
Integrating ERP and CRM systems creates a powerful unified platform that drives business success through seamless data flow and enhanced operational visibility. This strategic combination delivers multiple advantages:
Key Integration Benefits:
- Real-time data synchronization between customer-facing and back-office operations
- Elimination of duplicate data entry and manual updates
- Accurate pricing and inventory information across all customer touchpoints
- Enhanced forecasting capabilities through comprehensive data analysis
- Streamlined order-to-cash processes
Business Impact:
- Sales teams access accurate product availability and pricing
- Customer service representatives view complete customer histories
- Finance departments track orders and payments without switching systems
- Marketing teams leverage detailed customer purchase patterns
- Management gains 360-degree business insights for strategic planning
This integration establishes a cohesive ecosystem where customer interactions, inventory levels, financial data, and operational insights move in tandem seamlessly. This allows businesses to make informed decisions and provides superior customer experiences by ensuring information is accurate and accessible.
Conclusion: Choosing ERP vs CRM Based on Business Needs
Both ERP and CRM are essential for modern businesses, but they serve different functions. ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) and CRM (Customer Relationship Management): Which is right for your organization right now? Consider these key factors:
- For operations that focus on scale, ERP systems work wonders as they are the best fit for businesses that prioritize internal process optimization and resource management
- CRM solutions help organizations that adopt a customer-centric approach to thrive, which is typically best for companies focused on sales growth and relationship building
- As your business matures, you may need both systems. Consider your current challenges:
- Are internal operations and workflow a challenge for your business?
- Does your sales team need better tools to help them manage customer relationships?
So take that next step—evaluate your specific requirements, identify the appropriate vendors, and implement the solution that meets your business needs. Making the right choice will push your organization to the next level through increased efficiency and growth.
